Helium mass spectrometry leak detection using high-purity gas pipeline injection method
Date:2022-03-14 Views:4454
a. Test Purpose
Use a helium mass spectrometer to sense the trace amount of helium gas leaking into the system for leak detection, and determine the size of the leak rate according to the detected amount of helium gas. This method is applicable to all pipeline transportation systems of high-purity gases and special gases.
b. Related Terms and Explanations
Vacuum Degree: The degree of rarefaction of gas in a vacuum state, usually expressed by "high vacuum degree" and "low vacuum degree".
Vacuum Degree Units: Torr, Pa.
1 Torr = 1/760 atmosphere = 1 millimeter of mercury
1 Torr = 133.322 Pa
1 Pa = 7.5×10-3 Torr
Leak Rate: The rate at which substances leak in a closed vacuum space under the external standard atmospheric pressure and per unit time.
Common Units of Leak Rate: Pa.m3/sec, mbar.l/sec, atm.cc/s
10 Pa.m3/sec = 1 mbar.l/sec = 1 atm.cc/s
Molecular Pump: Through the high-speed rotating impeller, when gas molecules collide with the turbine blades, they are driven towards the air outlet and then pumped out by the fore pump.
c. Test Instrument
Helium Mass Spectrometer Leak Detector
d. Preparation before the Test
(1) The system has successfully passed the pressure holding leak detection.
(2) Confirm that all components of the system can withstand the vacuum state without damage.
(3) First, detect the leak rate of the valve group and connecting pipeline of the leak detector itself.
(4) Before connecting the leak detector to the system pipeline, release the gas in the system to be tested.
(5) Slowly open the valve at the inlet of the leak detector, and evacuate the pipeline between the leak detector and the pipeline system isolation valve until the background leak rate displayed by the leak detector is lower than 1× 10-9 mbar.l/s.
(6) Blow helium gas onto all the weld beads and mechanical connection points on the connecting pipeline.
(7) After confirming that there is no leak in the connecting pipeline, close the valve at the inlet of the leak detector.
e. Test Method
(1) Confirm that the pressure gauge on the system is a composite pressure gauge that can withstand negative pressure. If not, remove the pressure gauge and seal the port with a plug. Confirm that all the valves and pressure regulating valves in the system are fully open.
(2) Usually, the helium leak detection work requires two people, one to blow helium gas and the other to monitor the indication of the leak detector.
(3) Confirm that the pressure in the system is 0. If there is still positive pressure in the system, release the gas in the system first. Slowly open the isolation valve between the system and the leak detector.
(4) Slowly open the valve at the inlet of the leak detector and start to evacuate the system to a vacuum state. Operate according to the operation instructions of the leak detector until it reaches the detectable state.
(5) Record the background helium leak rate of the leak detector. The helium gas blowing work can only be carried out after the background helium leak rate is lower than 1 ×10-9 mbar.l/s.
(6) Do not perform the zero-clearing operation on the leak detector during the detection process.
Note: If helium gas or moisture is introduced into the system due to other reasons (such as improper detection or installation) before the leak detection test, the pipeline system should be purged with high-purity nitrogen to remove the helium gas or moisture so that the leak detection test can be successfully completed. If the background helium leak rate still cannot be reduced to below 1×10-9 mbar.l/s after 30 minutes, the tester can blow helium gas at the connection points to determine whether there is an obvious leak. If not, close the valve at the inlet of the leak detector, refill the system with high-purity nitrogen, continuously purge each part of the system at least once, and then continuously purge the system for 30 minutes before re-detection.
(7) Start the detection from the weld bead or connection point closest to the leak detector. Blow helium gas onto the weld bead or connection point with a spray gun so that the helium gas stays at the weld bead or connection point for a certain period of time. After confirming that there is no leak, proceed to the detection of the next weld bead or connection point until the last weld bead or connection point.
(8) If it is found that the indication value of the leak detector is rising, after the reading of the leak detector returns to normal, re-detect the weld bead or connection point to confirm whether there is really a leak. If it is confirmed that there is no leak at this weld bead or connection point, successively detect the weld beads or connection points before this weld bead or connection point until the leak point is found.
(9) Until all the connection points are detected, the qualified connection points should be pasted with qualified signs. After all the connection points have been blown with helium gas, continue to observe the reading of the leak detector for about 10 minutes. The system can be separated from the instrument only after confirming that the reading is normal.
(10) Close the valve at the inlet of the leak detector. If the helium leak rate of each connection point is lower than 1× 10-9 mbar.l/s (mBar l/sec), it indicates that the leak rate of the system meets the requirements. The tester can record the detection results in the detection report.
(11) Close the isolation valve of the system and separate the leak detector from the system.
Note: The operation of high-purity pipelines and components should comply with the relevant regulations of the owner to ensure that the pipelines and components are not contaminated or damaged.
Leak Detection Steps for Double-layer Pipelines:
(1) The outer pipe of the double-layer pipeline can only be welded after the inner pipe is installed and passes the inspection.
(2) The installation of the outer pipe of the double-layer pipeline does not require the same strict cleanliness quality as the installation of the inner pipe, so there is no need to conduct a cleanliness test, but the requirement for its airtightness test is still the same as that of the inner pipe.
The helium mass spectrometer leak detection steps for the outer pipe are the same as the above leak detection steps.
After the detection is completed, the outer pipe is either evacuated to a vacuum state (-30 in/hg) or filled with nitrogen at 60 PSIG (if the pipeline is equipped with a heating bag). Since the pipeline is equipped with a heating belt, the outer pipe should be filled with nitrogen at 60 PSIG. Continue to observe the pressure indicator/gauge on the outer pipe for 24 or 48 hours to confirm that the pressure does not change.
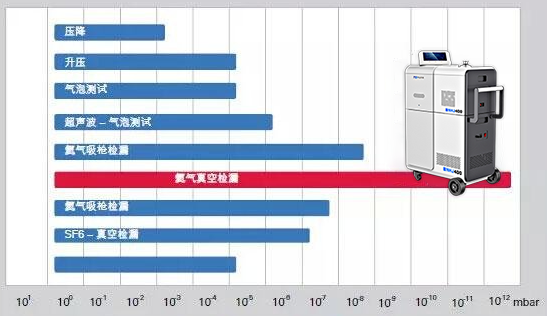
Anhui Nuoyi Technology provides a complete product line of helium mass spectrometer leak detectors, from portable helium mass spectrometer leak detectors to leak detection modules, providing negative pressure leak detection (vacuum method) and positive pressure leak detection (sniffer probe method) to meet various applications. Compared with traditional foam leak detection and differential pressure leak detection, the helium mass spectrometer leak detector can detect a smaller leak rate of 5E-13 Pa m3/s while providing non-destructive leak detection. Using helium gas as a tracer gas can accurately locate and quantify the leak points. The helium mass spectrometer leak detector can meet the needs of single-machine leak detection and can also be integrated into the leak detection system or PLC.








 Public Security Network Security Record in Anhui Province No. 34010302001915
Public Security Network Security Record in Anhui Province No. 34010302001915